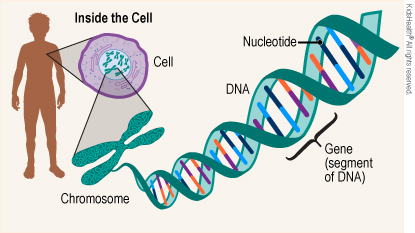
Genes are the basic segments of DNA that acts as a functional unit of heredity. Humans have around 20,000 to 25,000 genes. These instructions show how an organism lives and acts in their respective environments. Structures that contain the genes in a person are called chromosomes, which contain hundreds to thousands of genes. Number of chromosomes varies from species to species, for example humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes and a dog contains 78 of these chromosomes. Biological instructions contribute to the unique natures of animals from various environments. Through offspring genes and DNA are passed through the process of meiosis.
The genes are made up of 4 nucleotides Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine. Combinations of these nucleotides forms the code for different characteristics such as black hair or blue eyes. Alleles are alternative forms or versions of genes that are acquired from each parent of an offspring. Internal and external factors are impacted through these specifics and contribute to genetic diversity in species of life. Mutations of genes is a change in the sequence of DNA and causes a misspelling. An example of a mutation effect is in the HBB cell, where Sickle Cell Anemia can occur and where blood flow is derived, and nerves are damaged as a result. Genetic disorders are caused when there is a missing part of a chromosome, gene shifting from one chromosome to another, extra or missing chromosome, etc.
An international research project called The Human Genome Project was undertaken to map all the genes of humans. The project has benefited to help us detect early onset of diseases using genetic profile, helps to customize medication to fit the treatment, develop better yielding and disease resistant plants using their DNA sequencing, etc. The complete DNA sequencing of more and more organisms, including humans, will revolutionize biology and medicine. This study may answer age old questions such as how organisms evolved, whether synthetic life will ever be possible, and how to treat a wide range of medical disorders.
My References
https://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Human_Genome_Project_timeline.html